Can Someone With Short-Term Memory Loss Have Chronic Pain?
Reading time: 3 minutes
One of the most crucial things evidence-based chiropractors understand better than most is the connection between acute pain and chronic pain. Yes, chiropractors alleviate pain associated with specific tissue injury. However, many patient presentations encompass years of underlying chronic stressors, both physiologic and psychologic, leading to their current complaint. Solving these complex pain presentations is challenging; yet, rewarding for both the provider and patient.
Q: Can someone with short-term memory loss have chronic pain?
First: My Answer
Pain is both psychological and physiological. So, no, the patient won't remember having pain six minutes ago. However, their body will!The body will physiologically adapt to chronic pain regardless of central memory processing.
"…neural control of movement in vertebrates is located within spinal cord networks. Even without brain input, the spinal cord routinely uses feed-forward processing of sensory information, particularly proprioceptive and cutaneous, to continuously make fundamental decisions that define motor responses. In effect, these spinal networks may be largely responsible for executing coordinated sensorimotor tasks, even those under normal “conscious” control." (1)
Chronic pain is an outward manifestation of inner adaptations to pain processing. So yes, the brain IS responsible for pain perception and remembering pain patterns. Other areas, including the dorsal horn of the spinal cord and peripheral tissue can also LEARN to be in pain.
Learning is a physiologic process continuously happening at three main sites within the body. Each site adapts physiologically in response to constant stimulation.
PERIPHERAL LEARNING
Pain is an unpleasant sensation usually evoked by the activation of nociceptors in response to harmful high-intensity stimuli. What distinguishes the nociceptive system from other perceptual systems is its responsiveness to repeated stimuli. In innocuous stimuli, repetition typically reduces the response, a phenomenon referred to as HABITUATION. In contrast, repetition of a noxious stimulus can induce a progressive amplification of the usual response to the stimulus, i.e., SENSITIZATION. The nociceptive system tends to increase its responsiveness when exposed to repeated stimulation.
Habituation and sensitization are two necessary forms of non-associative learning. Habituation would generally allow a person to filter out irrelevant sensory input about their environment. Whereas sensitization would increase the ability to respond to stimuli, potentially compromising the organism's integrity and survival, thus fulfilling a protective role. (2)
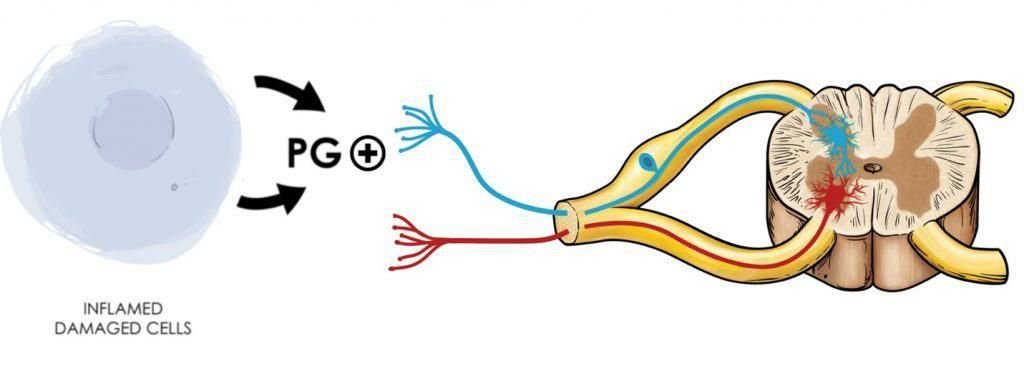
Fig 1. Pain perception begins with peripheral tissue irritation from a mechanical insult, heat, or chemical irritation. The affected tissue and surrounding immune cells start releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines like prostaglandins. Sensory nerve fibers (1st order neurons) will respond to prostaglandin stimulation and carry the signal or impulse to the spinal cord’s dorsal horn.
Second: The Webinar
Third: 6 Solutions To Chronic Pain
Solution 1: Manual Therapy
Pain from ongoing musculoskeletal pathology produces continual nociceptive input. Reducing peripheral pain utilizing manual therapy may prevent the centralization of symptoms. (3) Select the right treatment for the right patient. The ability to reduce tension and mobilize joints is paramount to the restoration of musculoskeletal function.
Solution 2: Spinal Manipulation
Chronic nonspecific LBP patients treated with spinal manipulation experience local and remote hypoalgesia along with improved pain and disability. (4) Spinal manipulation provides short-term analgesia and long-term pain reduction when supplemented with the appropriate rehab or ADL modification.
For the most recent literature review available for chronic pain with unique chiropractic perspectives, check out the condition reference in ChiroUp.
Solution 3: Diet
Metabolic interventions, such as low-carbohydrate or ketogenic diets, are promising new avenues for diminishing hyperexcitability of the CNS in chronic pain patients. (5) Changing someone's diet is difficult since eating is habitual. If you don't possess the time or knowledge to address dietary contributors, find someone in your area who does.
Some of your best referrals will come from functional medicine chiropractors and nutritionists. These healthcare providers play an integral role in your success in treating patients with chronic musculoskeletal complaints.
Solution 4: BMI
One molecular hallmark of caloric excess and obesity is chronic inflammation, particularly in visceral adipose tissue (VAT). Over time, obese VAT becomes increasingly populated by pro-inflammatory cells, and the proportion of anti-inflammatory regulatory cells declines. (6) Increasing your patient’s activity level has multiple benefits. Exercise will increase the descending inhibitory pathway while promoting healthy habits leading to weight loss.
Solution 5: Sleep
Among people with chronic pain, insomnia is highly prevalent, closely related to the mechanism of chronic pain, and characterized by low-grade neuroinflammation. (7) Consultation with a sleep specialist may help you and your patients understand the underlying mechanisms behind their insomnia. Remember, pain at night is a red flag and warrants further workup. However, pain limiting the ability to fall asleep may indicate chronic pain from psychological or musculoskeletal etiologies. (8)
Solution 6: CBD
The majority of clinical studies for treating intractable chronic pain with CBD typically utilized a combination of 1:1 CBD: THC, often in the form of the well-tolerated oromucosal spray. (9) A New Zealand study on the safety of CBD treatment in 400 non-cancer chronic pain patients indicated prolonged use resulted in self-reported improvements in pain and quality of life. (10)
If we accept the immense privilege of helping people understand their pain and how they can recover from it, then we are absolutely obliged to know what it is we are talking about and if that requires some serious work, then so be it. -Mick Thacker
Commentary
Traditional management of peripheral pain syndromes involves a combination of interventions, depending on the treating healthcare professional. The conventional biomechanical pain model assumes a direct linear link between the amount of structural damage and the pain experienced by the patient. According to this model, addressing the underlying pathology should reduce or completely resolve symptoms to restore normal function. However, chronic pain does not always adhere to this biomedical model of pain, as repeated stimulation may result in sensitization of peripheral and central neural circuitry. Thus, it is common to observe a discordance between the degree of structural damage and the number of symptoms experienced by the patient.
I hope that this blog inspired you to consider new strategies that attack all avenues. Our goal at ChiroUp is to provide you with the resource to simplify the delivery of clinical excellence.
Sign up for your FREE 14-day trial today to access the most up-to-date research on 100 other protocols and MORE!
-
Gerasimenko, Y., Sayenko, D., Gad, P., Liu, C. T., Tillakaratne, N., Roy, R. R., Kozlovskaya, I., & Edgerton, V. R. (2017). Feed-Forwardness of Spinal Networks in Posture and Locomotion. The Neuroscientist : a review journal bringing neurobiology, neurology and psychiatry, 23(5), 441–453.
Filbrich L, van den Broeke EN, Legrain V, Mouraux A. The focus of spatial attention during the induction of central sensitization can modulate the subsequent development of secondary hyperalgesia. Cortex. 2020 Mar 1;124:193-203.
Lluch Girbés, E., Meeus, M., Baert, I., & Nijs, J. (2015). Balancing “hands-on” with “hands-off” physical therapy interventions for the treatment of central sensitization pain in osteoarthritis. Manual Therapy, 20(2), 349–352. doi:10.1016/j.math.2014.07.017
Bond BM, Kinslow CD, Yoder AW, Liu W. Effect of spinal manipulative therapy on mechanical pain sensitivity in patients with chronic nonspecific low back pain: a pilot randomized, controlled trial. Journal of Manual & Manipulative Therapy. 2020 Jan 1;28(1):15-27.
Koh IJ, Kang BM, Kim MS, Choi KY, Sohn S, In Y. How Does Preoperative Central Sensitization Affect Quality of Life Following Total Knee Arthroplasty?. The Journal of Arthroplasty. 2020 Apr 10.
Stubbs, B. J., & Newman, J. C. (2020). Ketogenic diet and adipose tissue inflammation—a simple story? Fat chance! Nature Metabolism. doi:10.1038/s42255-019-0164-2
Nijs J, Malfliet A, Ickmans K, Baert I, Meeus M. Treatment of central sensitization in patients with ‘unexplained’chronic pain: an update. Expert opinion on pharmacotherapy. 2014 Aug 1;15(12):1671-83.
Nijs J, Mairesse O, Neu D, Leysen L, Danneels L, Cagnie B, Meeus M, Moens M, Ickmans K, Goubert D. Sleep disturbances in chronic pain: neurobiology, assessment, and treatment in physical therapist practice. Physical therapy. 2018 May 1;98(5):325-35.
Ueberall, M. A., Essner, U., Mueller-Schwefe, G. H. (2019). Effectiveness and Tolerability of THC:CBD Oromucosal Spray as Add-On Measure in Patients With Severe Chronic Pain: Analysis of 12-Week Open-Label Real-World Data Provided by the German Pain E-Registry. J. Pain Res. 12, 1577–1604. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S192174
Gulbransen, G., Xu, W., Arroll, B. (2020). Cannabidiol Prescription in Clinical Practice: an Audit on the First 400 Patients in New Zealand. BJGP Open. doi: 10.3399/Bjgpopen20x101010