Top Tips for Meralgia Paresthetica
Meralgia Paresthetica is a painful compressive neuropathy of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (LFCN), causing burning pain and paresthesia in the anterolateral thigh. (1-3)
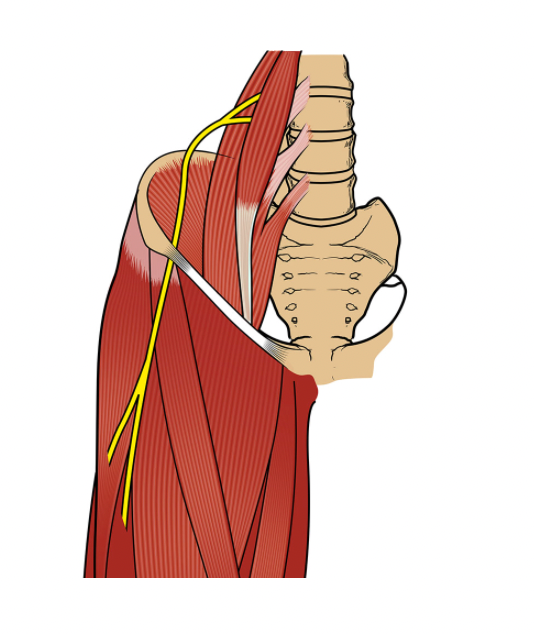
Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve
The LFCN splits directly from the lumbar plexus then runs through the pelvis, adjacent to the lateral border of the iliopsoas muscle, before passing beneath the lateral aspect of the inguinal ligament near the ASIS- which is also the most common site of entrapment. (4)
Watch the docs demonstrate the essential treatments, exercises, and nerve glides for meralgia paresthetica:
Meralgia Paresthetica Clinical Pearls
Prevalence & Incidence
Most common in middle-aged adults (5,6)
Diabetics have a nearly six-fold increased risk of developing the condition (7-9)
Present bilaterally in 20-25% of cases (5,10-12)
Affects men up to 3x more frequently than women (8,10-12)
Risk factors
Excessive compression or ischemic stretch of the LFCN is a primary etiological factor. (1,3) Obesity or recent weight gain often precedes the condition. (10,16-21) In fact, 8% of new cases report recent weight gains of more than 15 pounds. (10,22) The “COVID 15" weight gain concept will likely affect the incidence of this condition, as surveys suggest that worldwide, approximately one-third of adults have gained significant weight during the pandemic. (61) Other risk factors include:
Pregnancy
Carpentry tool belts, police duty belts, and soldier body armor (14,15)
Tight-fitting clothing, jeans, belts, or body-shaping undergarments
Direct trauma, including seat belt compression (23-25)
Extended periods of time lying prone on a hard surface (i.e. surgery) (26)
Presenting Symptoms
Complaints include pain, paresthesia, or hypersensitivity on the outside of the thigh described as dull, aching, itching, buzzing, or burning (1,3)
Symptoms may impair function and sleep (3,41)
Complaints are often provoked by walking and alleviated when sitting, as sitting may decrease tension on the inguinal ligament (11,12,41,42)
The primary site of tenderness is the emergence of the LFCN approximately one to two finger-widths inferior and medial to the ASIS. (44)
Clinical Findings
Tenderness over the lateral inguinal ligament in greater than 75% of cases (44)
Symptoms provoked by hip or lumbar extension and relieved by flexion (11,12,41,42)
Neurologic evaluation may demonstrate numbness or hyperesthesia over the distribution of the LFCN (41)
Pelvic compression test positive (sensitivity of 95% and a specificity of 93.3%)
LFCN Neurodynamic Test will likely reproduce symptoms (46,47)
Management
(Judicious) STM of the hip flexors, sartorius, TFL, quadriceps, and thigh adductors(52-57)
Nerve mobilization of the LCFN
Stabilization exercises for the core and pelvis (53-57)
Therapeutic exercise tape (60,61)
ADL Considerations
Losing weight
In some cases, simply wearing looser clothing may alleviate the complaint
Selective rest from aggravating activity (particularly repetitive hip flexion)
Carrying a toolbox instead of wearing a tool belt
Avoid wearing high heels (32)
Conclusion
Conservative management is the frontline treatment for meralgia paresthetica and is successful in up to 91% of cases. (16, 52, 53) The central goal of treatment is to remove any cause of excessive compression. (16, 52)
Review the ChiroUp Meralgia Paresthetica protocol for a complete best-practice synopsis.
ChiroUp subscribers can practice with confidence knowing that you’ve delivered the essential recommendations to help your patients recover quickly and effectively!
Not a ChiroUp Subscriber? Check out ChiroUp for 14 days for FREE!
-
Patijn J, Mekhail N, Hayek S, Lataster A, van Kleef M, Van Zundert J. Meralgia Paresthetica. Pain Pract. May-Jun 2011;11(3):302-8.
Bradley WG, Becker DP, editors. Neurology in Clinical Practice: The Neurological Disorders; Edited by Walter G. Bradley...[et Al.]; Associate Editors: Donald P. Becker...[et Al.]; with 131 Contributing Authors. Butterworth-Heinemann; 1991.
Grossman MG, Ducey SA, Nadler SS, Levy AS. Meralgia paresthetica: diagnosis and treatment. JAAOS-Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 2001 Sep 1;9(5):336-44. Link
Carai A, Fenu G, Sechi E, Crotti FM, Montella A. Anatomical variability of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve: findings from a surgical series. Clinical Anatomy: The Official Journal of the American Association of Clinical Anatomists and the British Association of Clinical Anatomists. 2009 Apr;22(3):365-70. Link
Harney D, Patijn J. Meralgia paresthetica: diagnosis and management strategies. Pain Medicine. 2007 Aug 20;8(8):669-77. Link
Martínez-Salio A, Moreno-Ramos T, Díaz-Sánchez M, Porta-Etessam J, de la Aleja González J, Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez G, Calandre-Hoenigsfeld L. Meralgia paraesthetica: a report on a series of 140 cases. Revista de neurologia. 2009;49(8):405-8. Link
Parisi TJ, Mandrekar J, Dyck PJ, Klein CJ. Meralgia paresthetica: relation to obesity, advanced age, and diabetes mellitus. Neurology. 2011 Oct 18;77(16):1538-42. Link
Van Slobbe AM, Bohnen AM, Bernsen RM, Koes BW, Bierma-Zeinstra SM. Incidence rates and determinants in meralgia paresthetica in general practice. Journal of neurology. 2004 Mar 1;251(3):294-7. Link
Harney D, Patijn J. Meralgia paresthetica: diagnosis and management strategies. Pain Medicine. 2007 Aug 20;8(8):669-77. Link
Ratliff JK et al. Meralgia Paresthetica Following Iliac Crest Bone Graft for Anterior Cervical Discectomy: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Department of Neurosurgery; Louisiana State University Medical Center; New Orleans, Louisiana. Accessed 9/18/14 from: www.medschool.lsuhsc.edu. Link
Mumenthaler M: Neurology. Thieme-Stratton, Inc., New York, 1983.
Sunderland S: Nerves and Nerve Injuries, ed 2. Churchill-Livingstone, New York, 1978.
Fargo MV, Konitzer LN. Meralgia paresthetica due to body armor wear in US soldiers serving in Iraq: a case report and review of the literature. Military medicine. 2007 Jun 1;172(6):663-5. Link
Korkmaz N, Özçakar L. Meralgia paresthetica in a policeman: the belt or the gun. Plastic and reconstructive surgery. 2004 Sep 15;114(4):1012-3. Link
Parisi TJ, Mandrekar J, Dyck PJ, Klein CJ. Meralgia paresthetica: relation to obesity, advanced age, and diabetes mellitus. Neurology. 2011 Oct 18;77(16):1538-42. Link
Mondelli M, Rossi S, Romano C. Body mass index in meralgia paresthetica: a case–control study. Acta neurologica scandinavica. 2007 Aug;116(2):118-23. Link
Chlebowski S, Bashyal S, Schwartz TL. Meralgia paresthetica: another complication of antipsychotic?induced weight gain. Obesity Reviews. 2009 Nov;10(6):700-2.
Moucharafieh R, Wehbe J, Maalouf G. Meralgia paresthetica: a result of tight new trendy low cut trousers (‘taille basse’). International Journal of Surgery. 2008 Apr 1;6(2):164-8. Link
Park JW, Kim DH, Hwang M, Bun HR. Meralgia paresthetica caused by hip?huggers in a patient with aberrant course of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve. Muscle & Nerve: Official Journal of the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine. 2007 May;35(5):678-80. Link
Sax TW, Rosenbaum RB. Neuromuscular disorders in pregnancy. Muscle & Nerve: Official Journal of the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine. 2006 Nov;34(5):559-71. Link
Ecker AD, Woltman HW. Meralgia paraesthetica: a report of one hundred and fifty cases. Journal of the American Medical Association. 1938 May 14;110(20):1650-2. Link
Beresford HR. Meralcia Paresthetica After Seatbelt Trauma. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery. 1971 Jul 1;11(7):629-30. Link
Blake SM, Treble NJ. Meralgia paraesthetica--an addition to'seatbelt syndrome'. Annals of the Royal College of Surgeons of England. 2004 Nov;86(6):W6. Link
Moscona AR, Sekel R. Post-traumatic meralgia paresthetica--an unusual presentation. The Journal of trauma. 1978 Apr;18(4):288-. Link
Cho KT, Lee HJ. Prone position-related meralgia paresthetica after lumbar spinal surgery: a case report and review of the literature. Journal of Korean Neurosurgical Society. 2008 Dec;44(6):392. Link
Kho KH, Blijham PJ, Zwarts MJ. Meralgia paresthetica after strenuous exercise. Muscle & Nerve: Official Journal of the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine. 2005 Jun;31(6):761-3. Link
MacGregor J, Moncur JA. Meralgia paraesthetica--a sports lesion in girl gymnasts. British journal of sports medicine. 1977 Apr 1;11(1):16-9. Link
Szewczyk J, Hoffmann M, Kabelis J. Meralgia paraesthetica beim Bodybuilder. Sportverletzung· Sportschaden. 1994 Jan;8(01):43-5. Link
Ulkar B, Yildiz Y, Kunduracio?lu B. Meralgia paresthetica: a long-standing performance-limiting cause of anterior thigh pain in a soccer player. The American journal of sports medicine. 2003 Sep;31(5):787-9. Link
Otoshi K, Itoh Y, Tsujino A, Kikuchi S. Case report: meralgia paresthetica in a baseball pitcher. Clinical orthopaedics and related research. 2008 Sep 1;466(9):2268. Link
Ahmed A. Meralgia paresthetica and femoral acetabular impingement: a possible association. Journal of clinical medicine research. 2010 Dec;2(6):274. Link
Goel A. Meralgia paresthetica secondary to limb length discrepancy: case report. Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation. 1999 Mar 1;80(3):348-9. Link
Ivins GK. Meralgia paresthetica, the elusive diagnosis: clinical experience with 14 adult patients. Annals of surgery. 2000 Aug;232(2):281. Link
Mumenthaler M: Neurology. Thieme-Stratton, Inc., New York, 1983.
Sunderland S: Nerves and Nerve Injuries, ed 2. Churchill-Livingstone, New York, 1978.
Turek SL: Orthopedics: Principles and Their Application, ed 4. J.B. Lippincott, New York, 1984.
Mohr JP, editor. Manual of Clinical Problems in Neurology: With Annotated Key References. Little, Brown Medical Division; 1989.
Kramer J: Intervertebral Disc Disease: Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prophylaxis. Year Book Medical Publishers, Chicago, 1981.
Bradley WG, Daroff RB, Fenichel GM, and Marsden CD: Neurology in Clinical Practice: The Neurological Disorders. Butterworth-Heinemann, Boston, 1991.
Nouraei SR, Anand B, Spink G, O'Neill KS. A novel approach to the diagnosis and management of meralgia paresthetica. Neurosurgery. 2007 Apr 1;60(4):696-700. Link
Elizabeth A Sekul Meralgia Paresthetica Clinical Presentation. Medscape. Accessed 9/3/2014. from: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1141848-clinical. Link
Ruige JB, De Neeling JN, Kostense PJ, Bouter LM, Heine RJ. Performance of an NIDDM screening questionnaire based on symptoms and risk factors. Diabetes Care. 1997 Apr 1;20(4):491-6. Link
Mumenthaler M: Neurology. Thieme-Stratton, Inc., New York, 1983.
Nouraei SR, Anand B, Spink G, O'Neill KS. A novel approach to the diagnosis and management of meralgia paresthetica. Neurosurgery. 2007 Apr 1;60(4):696-700. Link
Butler DS. The sensitive nervous system. Noigroup publications; 2000.
Butler DS, editor. The neurodynamic techniques: a definitive guide from the Noigroup team. Noigroup publications; 2005.
Nouraei SR, Anand B, Spink G, O'Neill KS. A novel approach to the diagnosis and management of meralgia paresthetica. Neurosurgery. 2007 Apr 1;60(4):696-700. Link
El-tantawi GA. Reliability of sensory nerve-conduction and somatosensory evoked potentials for diagnosis of meralgia paraesthetica. Clinical Neurophysiology. 2009 Jul 1;120(7):1346-51. Link
Kramer J: Intervertebral Disc Disease: Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prophylaxis. Year Book Medical Publishers, Chicago, 1981.
Kornbluth, Ira, and Pillip J. Marone. "Meralgia Paresthetica." eMedicine. Eds. Miguel A. Schmitz, et al. 9 Mar. 2009. Medscape. 9 Dec. 2009
Kadel RE, Godbey WD, Davis BP. Conservative and chiropractic treatment of meralgia paresthetica: review and case report. Journal of manipulative and physiological therapeutics. 1982 Jun;5(2):73-8. Link
Skaggs CD, Winchester BA, Vianin M, Prather H. A manual therapy and exercise approach to meralgia paresthetica in pregnancy: a case report. Journal of chiropractic medicine. 2006 Sep 1;5(3):92-6. Link
Houle S. Chiropractic management of chronic idiopathic meralgia paresthetica: a case study. Journal of chiropractic medicine. 2012 Mar 1;11(1):36-41. Link
Kalichman L, Vered E, Volchek L. Relieving symptoms of meralgia paresthetica using Kinesio taping: a pilot study. Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation. 2010 Jul 1;91(7):1137-9. Link
Kase K. Clinical therapeutic applications of the Kinesio (! R) taping method. Albuquerque. 2003.
Khalil N, Nicotra A, Rakowicz W. Treatment for meralgia paraesthetica. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2012(12). Link
Harney D, Patijn J. Meralgia paresthetica: diagnosis and management strategies. Pain Medicine. 2007 Aug 20;8(8):669-77. Link
Hurdle MF, Weingarten TN, Crisostomo RA, Psimos C, Smith J. Ultrasound-guided blockade of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve: technical description and review of 10 cases. Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation. 2007 Oct 1;88(10):1362-4. Link
Tumber PS, Bhatia A, Chan VW. Ultrasound-guided lateral femoral cutaneous nerve block for meralgia paresthetica. Anesthesia & Analgesia. 2008 Mar 1;106(3):1021-2. Link
Fowler IM, Tucker AA, Mendez RJ. Treatment of meralgia paresthetica with ultrasound?guided pulsed radiofrequency ablation of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve. Pain Practice. 2012 Jun;12(5):394-8. Link
Nicholas Rizzo N. Quarantine Weight Gain: 35.82% Gained Weight During Pandemic [19,903 Person Study] RunRepeat Blog. Posted on 20 January, 2021 Accessed from: https://runrepeat.com/quarantine-15-weight-gain-study